Leave Your Message
-
Phone
-
E-mail
-
Whatsapp
In the evolving landscape of technology, selecting the right optical sensor for your project is crucial. According to a recent report by MarketsandMarkets, the optical sensor market is expected to reach $25 billion by 2026. This growth underscores the increasing demand for high-quality imaging and sensing technologies across various industries. Optical sensors are critical in applications ranging from automotive to healthcare.
When making a choice, consider the specific requirements of your project. Each sensor type has distinct features and limitations. Some sensors excel in low-light conditions, while others may provide exceptional resolution in bright environments. It’s essential to identify what fits best for your intended use.
However, the decision can be overwhelming. Many projects falter due to selecting an incorrect sensor type or miscalculating the necessary specifications. A deeper understanding of each optical sensor's strengths and weaknesses can help mitigate this risk. In a world driven by precision and performance, the right choice can significantly impact project outcomes.
Optical sensors are essential in various applications, from industrial automation to consumer electronics. These sensors detect light and convert it into an electrical signal. Understanding the basics of how they function is crucial for any project.
Different types of optical sensors exist, such as photodiodes, phototransistors, and CCD sensors. Each has unique benefits and drawbacks. For instance, photodiodes offer high-speed response times and are commonly used in fiber optic communication. However, their sensitivity can be a double-edged sword; they may pick up unwanted ambient light, leading to inaccuracies. According to a 2022 market report, the optical sensor market is projected to grow at a CAGR of 10.5%, driven mainly by advancements in automotive and IoT sectors.
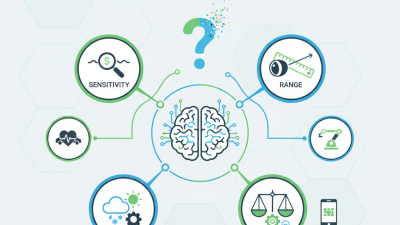
The choice of optical sensor also depends on specific project requirements. Factors such as light wavelength, sensitivity, and environmental conditions must be considered. For example, a sensor operating in harsh weather may require protection against moisture and dust, while a low-light application would need a sensor capable of detecting minimal light levels. Reflections and interferences can also complicate sensor performance, making testing and calibration vital steps. Understanding these nuances can significantly impact project success.
Choosing the right optical sensor can dramatically impact your project's success. Optical sensors come in various types, each with unique applications. Common types include CCD sensors, CMOS sensors, and photodiodes. CCD sensors are widely used in imaging applications, offering high-quality images. They excel in low-light conditions. CMOS sensors are cost-effective and efficient, making them popular in mobile devices. Photodiodes, on the other hand, are crucial in detecting light levels and converting them to electrical signals.
Many reports from industry analysts project substantial growth. The optical sensor market is expected to reach $30 billion by 2026, reflecting increasing demand in automotive and industrial sectors. Understanding the application of each sensor type will guide you in your decision-making process.
Tip: Assess environmental conditions before selecting a sensor. Some sensors may struggle with extreme temperatures or humidity.
Another consideration is the resolution required for your project. Higher resolution sensors can capture more detail but may increase costs. Balance performance needs with your budget constraints.
Tip: Always prototype with different sensor types. This can reveal unexpected performance issues or advantages. Insights gained from hands-on testing can be invaluable for final decisions.
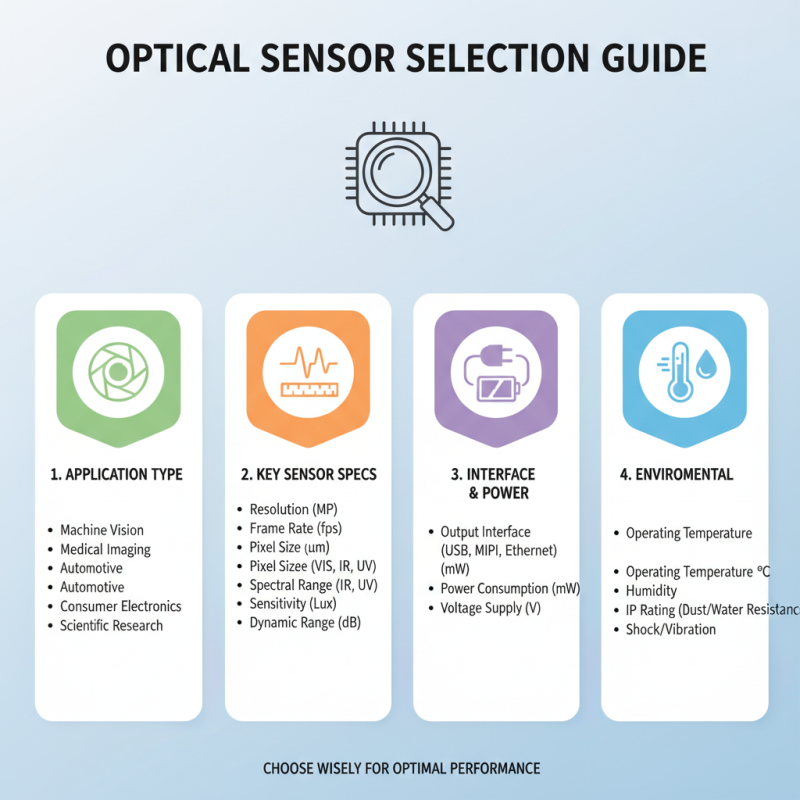
Choosing the right optical sensor is crucial for any project. Different applications require different sensor specifications. Here are some key factors to consider.
Start by assessing your project's light conditions. Will it operate in bright sunlight or dim environments? The sensor's sensitivity to light will vary based on this. For outdoor use, consider sensors with a higher dynamic range. For indoor applications, standard sensors may suffice.
**Tip:** Test different sensors in real conditions. You may be surprised by their performance variations.
Think about the type of measurements you need. Do you require color detection, distance measurement, or motion sensing? Each function demands specific optical sensor capabilities. Research how your chosen sensor handles these tasks.
**Tip:** Create a list of required features. This simplifies your decision-making process.
Finally, evaluate the sensor's size and integration ease. Are you working with limited space? Consider compact sensors. Check how easily they combine with your existing systems. Compatibility can affect project timelines and costs.
**Tip:** Don’t rush your selection. Take the time to prototype. Early mistakes can lead to costly redesigns later.
When selecting an optical sensor, understanding specifications is crucial. Consider parameters like resolution, sensitivity, and dynamic range. For example, a report from the Optical Society indicates that sensors with higher resolutions can capture more detail, which is essential for precision tasks. Sensitivity measures how well a sensor detects light, impacting its performance in low-light conditions. Dynamic range describes the sensor's ability to handle bright and dark areas in the same scene.
Tips: Always assess environmental factors. Sensors exposed to varying temperatures might yield inaccurate readings. Evaluate your project’s specific light conditions too. Not all sensors perform equally in artificial light versus natural light.
Some specifications can be misleading. A sensor may boast high sensitivity but can produce noise. This noise can detract from image quality. Moreover, not every high-resolution sensor fits every application. Sometimes, a lower resolution sensor with better noise control is preferable. Test various sensors in your project's real-world conditions. This reflection can reveal weaknesses in claimed specifications.
Integrating optical sensors into your system design requires careful consideration. These sensors can enhance functionality but may introduce complexities. Selecting the right type is critical. There are many options, including photodiodes and CCD sensors. Each has unique strengths and limitations.
When embedding these sensors, think about your project’s specific needs. Placement matters. Is there enough light where the sensor will be positioned? What environment will it operate in? These factors affect performance. Sometimes, a sensor that seems perfect on paper can struggle in real-world applications.
Testing is essential. Prototype your design and observe sensor behavior. This phase can reveal unexpected issues. Adjustments might be needed to enhance sensitivity or reduce noise. Document your findings, as they will inform future projects. Engaging with the data thoroughly can lead to better decisions.
| Sensor Type | Resolution | Sensitivity | Field of View | Power Consumption | Cost |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CCD Sensor | 12 MP | High | 90 degrees | 2 W | $150 |
| CMOS Sensor | 10 MP | Medium | 75 degrees | 1 W | $100 |
| LiDAR Sensor | High Definition | Very High | 360 degrees | 3 W | $1200 |
| Infrared Sensor | Lower Resolution | High | Narrow | 0.5 W | $50 |
| Time-of-Flight Sensor | High Definition | Medium | Wide | 1.5 W | $300 |