Leave Your Message
-
Phone
-
E-mail
-
Whatsapp
In the rapidly evolving field of automation and control systems, selecting the appropriate photoelectric sensor can significantly influence the success of your project. As noted by industry expert Dr. Emily Carter, a leading figure in sensor technology, “The right photoelectric sensor not only enhances efficiency but also improves precision in various applications.” With countless options available, understanding the key factors in choosing the right device is crucial for engineers and project managers alike.
Photoelectric sensors are known for their reliability and versatility, making them essential components in a wide range of industries, from manufacturing to logistics. Their ability to detect objects without physical contact provides unique advantages, but it also presents challenges when it comes to selection. Factors such as sensing distance, environmental conditions, and output type must be considered to ensure optimal performance.
In this article, we will explore the top ten tips for choosing the right photoelectric sensor for your projects. By following these guidelines, you can streamline your decision-making process and ultimately enhance the overall functionality of your systems.
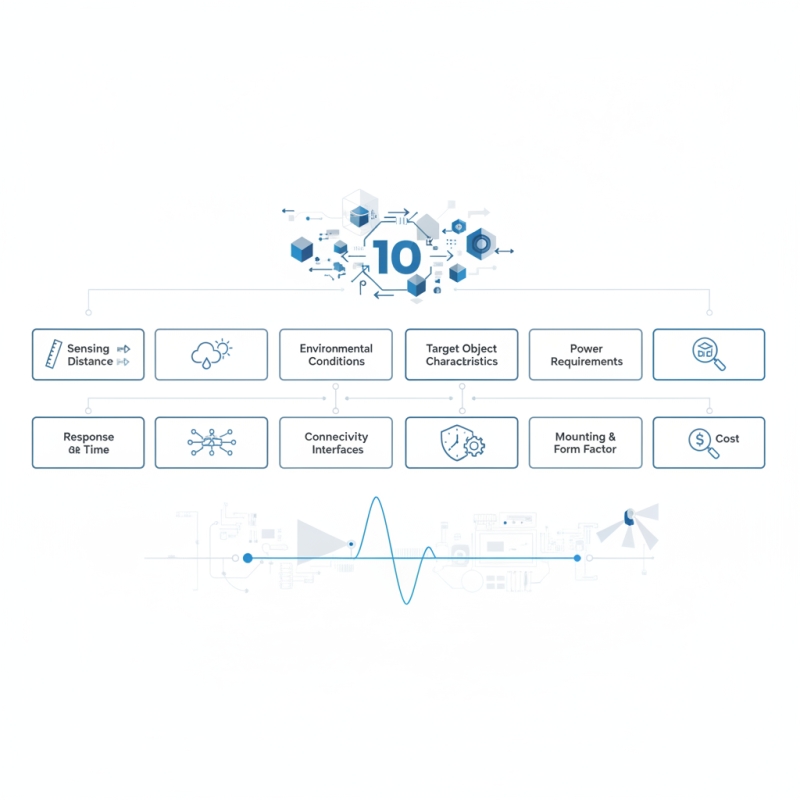
Photoelectric sensors are essential components in automation and control systems, widely used for detecting the presence or absence of objects without physical contact. They operate on principles such as reflection, refraction, and light interruption and can be categorized into four main types: through-beam, reflective, diffuse, and scatter. Each type has unique advantages tailored to specific applications; for instance, through-beam sensors offer long-range detection and are ideal for high-speed operations, while diffuse sensors are suitable for close-range detection in compact spaces, showcasing versatility across various environments.
According to a recent industry report by MarketsandMarkets, the global photoelectric sensor market is projected to reach USD 2.77 billion by 2025, growing at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 6.1% from 2020. This growth is driven by the increasing adoption of automation across industries such as manufacturing, packaging, and automotive. As these sectors evolve, photoelectric sensors have also become integral in robotics and machine vision applications, facilitating streamlined processes and enhanced operational efficiency.
Understanding the distinct functions and benefits of each sensor type is crucial for engineers and project managers in selecting the right solution, ultimately ensuring effective integration into their automated systems.
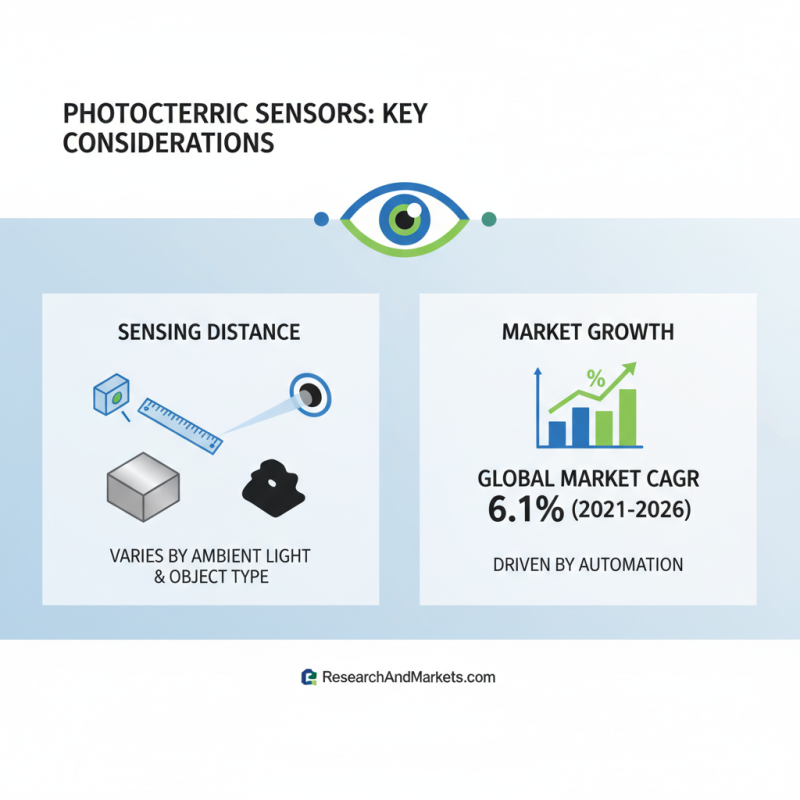
When selecting a photoelectric sensor for your projects, one of the key specifications to consider is the sensing distance. Sensors need to be evaluated based on their application environment, as the sensing range can vary significantly depending on factors such as ambient light and the type of object being detected. A report from ResearchAndMarkets.com indicates that the global photoelectric sensor market is expected to grow at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 6.1% between 2021 and 2026, reflecting the increasing reliance on automation and advanced sensing technologies across various industries.
Another critical specification is the sensing mode, which includes retroreflective, diffuse, and through-beam configurations. Each mode has its unique advantages and limitations that can affect performance in specific applications. For instance, if you are working in a cluttered environment, a diffuse mode might be preferable due to its versatile detection capability. According to recent data from the International Society of Automation, 87% of automation professionals agree that understanding these modes is essential for optimizing sensor performance in their specific contexts.
When choosing a photoelectric sensor, consider the environmental conditions such as temperature, humidity, and exposure to contaminants. Sensors rated for harsh environments can ensure longevity and reliability in challenging conditions. Additionally, evaluate the output type that best suits your project needs—whether it’s PNP, NPN, or analog—to ensure compatibility with your existing systems. Implementing these tips will significantly streamline your selection process and enhance the effectiveness of your automation projects.
When selecting a photoelectric sensor for your projects, it is crucial to assess environmental conditions that may affect sensor performance. Factors such as temperature, humidity, and the presence of dust or moisture can drastically impact the accuracy and longevity of these devices. According to industry reports, nearly 30% of sensor failures can be traced back to environmental factors that were not adequately evaluated before installation. This highlights the importance of conducting a thorough assessment to ensure that the chosen sensor is suitable for the specific conditions it will face.
One important tip for navigating these environmental conditions is to consider the sensor's operating temperature range. Ensure that the sensor can withstand both the lowest and highest temperatures it may encounter in its operational setting. Additionally, look for sensors that have protective enclosures or ratings that are appropriate for applications in wet or humid environments, such as IP ratings. Another consideration is to evaluate the level of ambient light in the environment, as strong interference can lead to sensor misreads. A sensor with an adjustable sensitivity setting can be beneficial in minimizing such disturbances.
Lastly, be mindful of physical obstacles within the environment that may block the sensor's line of sight. Conducting a site survey to identify these elements can save significant time and resources in the long run. By accounting for these factors, you'll be setting a solid foundation for the successful integration of photoelectric sensors in your projects, ultimately enhancing their reliability and performance.
When budgeting for photoelectric sensors in your projects, it’s crucial to strike a balance between cost and value. Industry reports indicate that the average cost of photoelectric sensors can vary widely, ranging from as low as $25 to over $200, depending on their specifications and functionalities. According to a recent market analysis, the global photoelectric sensor market is projected to grow at a CAGR of 6.5% between 2021 and 2026, which underscores the increasing demand for high-quality sensors across various sectors. This growth may indicate that investing in premium sensors could yield more significant returns through improved performance and reliability.
Understanding the specific requirements of your project is essential to determine the right sensor within your budget. For example, sensing range, environmental resilience, and response time are critical factors that drive the cost. A study by the Automation Industry Association found that while cheaper sensors may reduce initial expenditures, they often result in higher maintenance costs and lower efficiency in the long run. Hence, a thorough analysis of total cost of ownership (TCO) should inform your purchasing decision, allowing you to select a sensor that not only fits your immediate budget but also aligns with your project's long-term objectives. By carefully evaluating the cost-value ratio, you can make a more informed decision that meets both your financial and operational needs.
When selecting a photoelectric sensor for your projects, ensuring integration and compatibility with existing systems is crucial for seamless operation. Many industries rely heavily on automation, and according to a report from the International Society of Automation, approximately 60% of manufacturing processes currently utilize sensors to enhance efficiency and reduce errors. Therefore, verifying that your chosen sensor works with existing protocols and hardware is essential in avoiding costly disruptions.
One important tip is to assess the communication interfaces your current systems employ, such as Ethernet, RS-232, or fieldbus technologies. Make sure the sensor you choose can communicate effectively with these interfaces to facilitate data exchange and monitoring. Additionally, consider the power supply requirements; selecting sensors that can operate on the same voltage levels as your existing equipment reduces installation complexity and enhances reliability.
Another key point is understanding environmental compatibility. Sensors in industrial settings often face harsh conditions. It’s advisable to opt for photoelectric sensors with IP ratings that match the environmental demands of your application. For instance, a study by MarketsandMarkets indicates that over 25% of sensor failures are attributed to environmental influences. Choosing a sensor designed to withstand factors like moisture, dust, and temperature fluctuations ensures sustained performance without frequent replacements.
