Leave Your Message
-
Phone
-
E-mail
-
Whatsapp
Rotary Encoders play a crucial role in precise position measurement. They convert the mechanical motion of a rotating shaft into electronic signals. As Fred Johnson, a renowned expert in motion control, once stated, "A Rotary Encoder is essential for accurate feedback in automated systems." This highlights the significance of these devices in various applications, from robotics to industrial automation.
Using a Rotary Encoder can be straightforward, yet there are complexities involved. Installation requires careful attention to alignment. Even slight errors can lead to inaccurate readings. Choosing the right type of Rotary Encoder is vital for your specific needs. Some encoders offer higher resolution, while others are more cost-effective.
There is often a lack of understanding in troubleshooting common issues. Users may overlook factors like environmental interference or wiring problems. These mistakes can lead to frustrating inaccuracies. So, developing a solid foundation in Rotary Encoder technology is essential for better results. Attention to detail makes a significant difference in performance.
Rotary encoders are essential devices for accurate position measurement. They convert the angular position or motion of a shaft into an electrical signal. There are mainly two types: incremental and absolute encoders. Incremental encoders measure changes in position, providing relative data. They require a reference point to ensure accuracy. This can lead to errors if not properly calibrated.
Absolute encoders, on the other hand, provide a unique output for each position. They maintain their position information even when power is lost. This feature is useful in applications where precision is critical. However, they tend to be more complex and costly than incremental encoders.
Understanding these differences is crucial when selecting an encoder for your project. The choice will depend on your application's specific needs. Sometimes, the decision can feel overwhelming. Each type has its pros and cons. Balancing cost, complexity, and accuracy is essential for an effective solution.
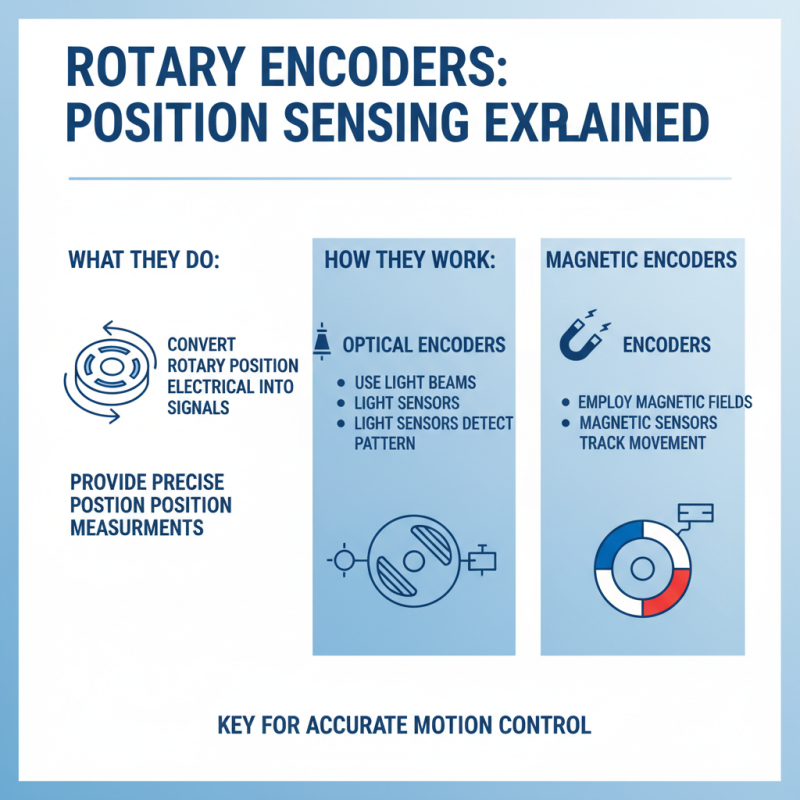
Rotary encoders are essential in various applications, providing precise position measurements. They convert rotary position into an electrical signal. Understanding their operating principles reveals why they are so effective. These devices typically use either optical or magnetic methods to detect rotation. Optical encoders utilize light beams and sensors to determine position. Meanwhile, magnetic encoders rely on magnetic fields for tracking movement.
Recent industry reports indicate that rotary encoders can achieve resolution levels up to 16,384 pulses per revolution (PPR). This high precision is vital in robotics and automation systems. However, environmental factors can affect performance. Dust, temperature fluctuations, and moisture can introduce errors. Sometimes, maintenance is overlooked, leading to sensor drift and inaccuracies over time.
The adaptability of rotary encoders enhances their utility. They can be integrated into various mechanisms, from simple machines to complex automation systems. Yet, challenges remain in signal processing and noise reduction. Implementing error-correcting algorithms may be necessary. Failure to address these issues can lead to compromised accuracy and increased operational costs. Manufacturers continue to innovate solutions for better performance and reliability in challenging conditions.
Setting up a rotary encoder for measurement applications requires careful attention to detail. Start by selecting the right encoder type. Incremental and absolute encoders serve different purposes. For precise measurements, absolute encoders are more suitable. They provide a unique position value each time, making them invaluable for applications demanding high accuracy.
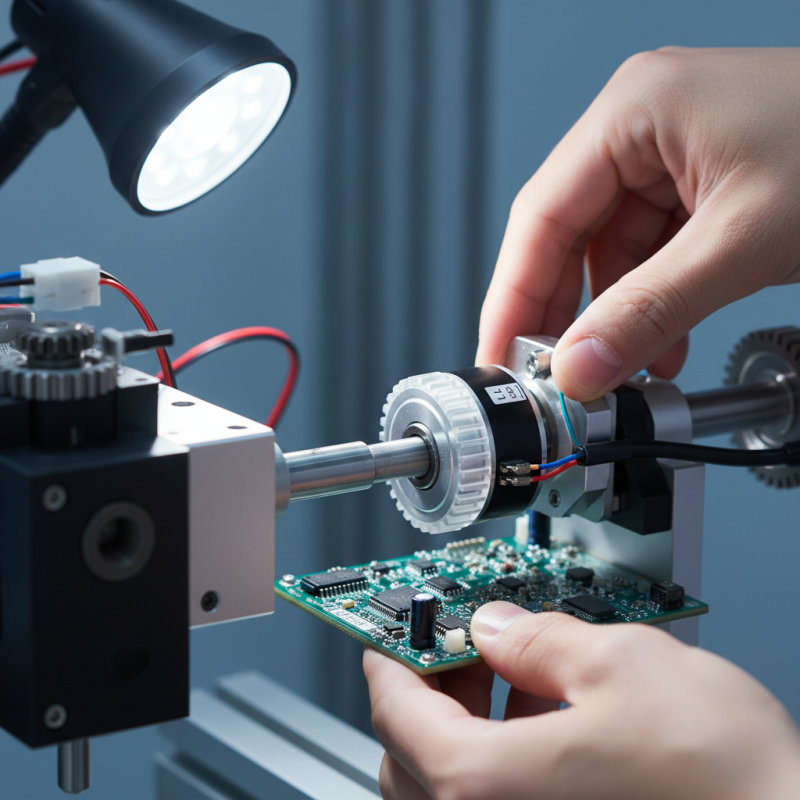
Mounting the encoder correctly is crucial. Misalignment can lead to inaccurate readings. Ensure that the encoder shaft is aligned directly with the component it measures. Avoid any significant angular deviation. According to industry reports, even small misalignments can result in errors exceeding 1%. This emphasizes the importance of proper installation.
Tips: Use a firm and stable mounting environment. This reduces vibrations that can affect measurements. Always refer to the encoder's specifications for optimal parameters. Regular calibration is also essential. It’s easy to neglect this step, but even slight drifts over time can impact performance. Remember, measurement accuracy is not just about equipment but how well it’s set up and maintained.
Calibration techniques are essential for achieving accurate position measurement with rotary encoders. A well-calibrated encoder ensures that the position feedback is reliable. Industry studies indicate that improper calibration can lead to errors of up to 10%. This can significantly impact applications where precision is crucial, such as robotics and CNC machining.
To calibrate effectively, one must consider the encoder's installation environment. Factors like temperature, humidity, and vibration can affect accuracy. Regularly running calibration tests is advisable. For instance, a common technique involves using a known reference point. This can help in adjusting the encoder’s readout to match the actual position.
However, it’s important to remember that calibration is not a one-time task. Encoders can drift over time. Regular maintenance schedules are necessary to address this. A checklist for calibration can include monitoring mechanical wear, checking connections, and assessing sensor alignment. These steps may seem tedious but are vital for maintaining accuracy in measurement tasks.
| Calibration Technique | Description | Accuracy Improvement (%) | Common Use Cases |
|---|---|---|---|
| Zero Point Calibration | Set the initial reference position to ensure accurate readings. | 95% | Robotics, CNC Machinery |
| Linear Calibration | Adjust encoder readings along a known length for accuracy. | 90% | Industrial Automation, Conveyor Systems |
| Multi-Point Calibration | Calibrate at multiple points to create a curve for compensation. | 98% | Precision Equipment, Research Instruments |
| Software Compensation | Use algorithms to correct systematic errors in readings. | 85% | Sensor Networks, Automated Control Systems |
| Temperature Compensation | Adjust readings based on thermal changes affecting the encoder. | 92% | Aerospace, Automotive Testing |
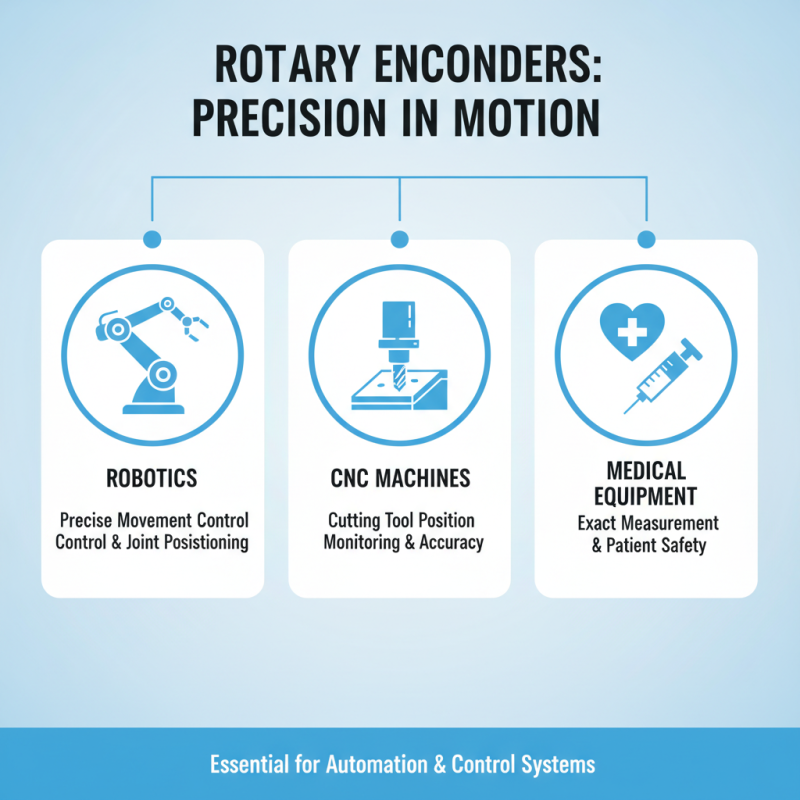
Rotary encoders play a crucial role in various industries and applications. Commonly, they are used in robotics for precise movement control. In CNC machines, they monitor the position of the cutting tool, ensuring accuracy. They also find use in medical equipment, where exact measurements can be a matter of safety.
In the automotive field, rotary encoders track steering angle and wheel rotation. This data aids in providing stability and enhances vehicle safety features. Elevators use rotary encoders for position sensing, allowing for smooth stops at each floor. These applications highlight the versatility of rotary encoders in modern technology.
Tips: When selecting a rotary encoder, consider the environment. Dust or moisture can impact performance. Regular calibration is essential to maintain accuracy over time. Avoid over-complicating the setup; a simpler system can often be more reliable. Don't forget to test thoroughly after installation.