Leave Your Message
-
Phone
-
E-mail
-
Whatsapp
In the realm of modern power control, the Zero Crossing Relay (ZCR) stands out for its efficiency. John Smith, a leading expert in electrical engineering, once stated, “Using a Zero Crossing Relay can significantly reduce energy losses.” This technology enables reliable switching with minimal interference.
The key advantage of a Zero Crossing Relay is its ability to synchronize with the AC waveform. This synchronization minimizes voltage spikes, extending the life of connected devices. Many industries are adopting ZCRs for various applications, ranging from heating elements to lighting control. However, user error can still occur. Understanding the specific connections and load requirements is crucial.
Not every application benefits from ZCRs. Users should contemplate whether the added complexity justifies the efficiency gains. Even experienced engineers can overlook details during implementation. By reflecting on these challenges, we can optimize the use of Zero Crossing Relays for better power management in various settings.

Zero crossing relays (ZCRs) play a pivotal role in efficient power control. By controlling the timing of electrical signals, ZCRs minimize electrical noise and extend the lifespan of equipment. The primary function of a ZCR is to switch on and off at the point where the AC voltage crosses zero. This method reduces inrush current and helps in avoiding voltage spikes.
According to industry reports, implementing ZCRs can enhance energy efficiency by up to 30%. This is crucial for industries focused on reducing operational costs. Users can expect lower heating in cables and components, leading to longer service life. However, improper handling of ZCRs might result in unintended system failures. It's important to carefully calculate load requirements.
Tip: Regularly inspect components connected to a zero crossing relay. Ensure they can handle high inrush currents.
ZCRs can be complex, especially for new users. Understanding their operation is essential. You may find that calibration can be tricky. Adjustments are necessary to align them with specific applications.
Tip: Always consult technical documents when using ZCRs. Do not overlook safety protocols during installation.
Embracing zero crossing technology can yield significant benefits. The key lies in proper usage and understanding the potential pitfalls.
Zero crossing relays play a crucial role in power control systems. They switch on and off at the exact moment the AC signal crosses zero volts. This timing reduces electrical noise and enhances system efficiency. One notable benefit is less heat generation, which results in longer component life. Devices operate quietly and smoothly. Such features make them ideal for home automation and industrial applications.
Another advantage lies in energy savings. By minimizing inrush currents, these relays help reduce overall power consumption. The relay's design allows for rapid switching, which is essential for precise power management. Users often report improved performance in their devices. However, some may find installation challenging. Proper configuration is necessary to achieve optimal results. Despite these hurdles, the benefits typically outweigh the learning curve. Adapting to new technology can be daunting but rewarding in the long run.
| Feature | Description | Benefits |
|---|---|---|
| Zero Crossing Detection | The relay detects the exact point where the AC signal crosses zero voltage. | Reduces electrical noise and voltage spikes, prolonging the lifespan of devices. |
| High Efficiency | Operates at set intervals to ensure minimal power loss during transitions. | Improves overall energy efficiency in power control applications. |
| Wide Compatibility | Works with various AC loads, including resistive, inductive, and capacitive. | Versatile option for numerous applications, from home automation to industrial controls. |
| Cost-Effective | Low maintenance and easy installation for efficient power management. | Reduces installation and operational costs in power control systems. |
| Improved Safety | Minimizes the risk of electrical hazards by switching at safe points in the AC cycle. | Promotes safer operation for both users and equipment. |
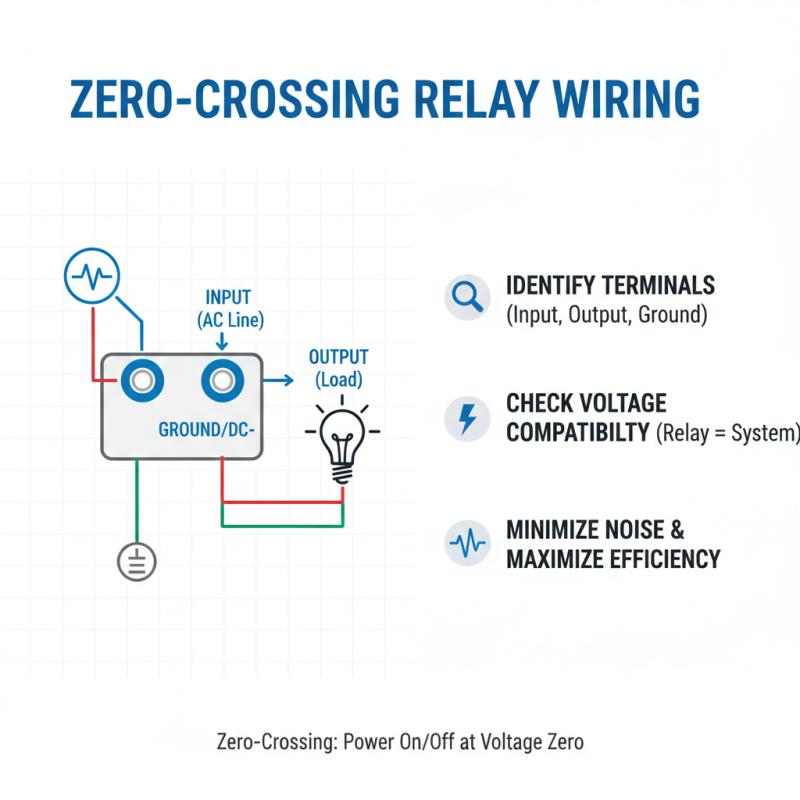
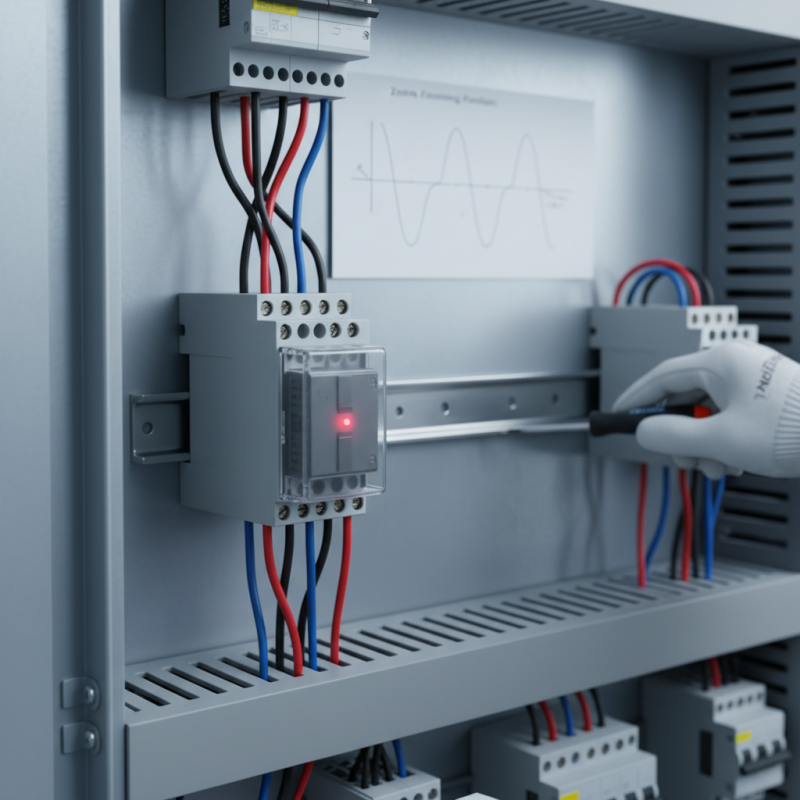
Wiring a zero crossing relay requires careful attention. This type of relay turns on and off when the voltage crosses zero. It minimizes electrical noise and increases control efficiency. Start by identifying the relay's terminals. There are usually three: input, output, and ground. Confirm that your relay matches the voltage of your system.
Next, take your time to connect the input to your control device. Use appropriate gauge wires to handle the current. Secure the output to the load, ensuring no exposed wires. Ground your relay to prevent electrical shock. Check connections before powering on. A loose connection can lead to malfunction.
Make sure to observe the relay during initial use. Unexpected sounds or overheating may signal issues. Do not ignore these signs. Look over your wiring again. Sometimes, things aren’t perfect at first. Adjustments might be needed. Learning from these experiences will refine your skills. Pay attention to details to improve efficiency.
Using a zero crossing relay can greatly enhance power control efficiency. It manages the electrical load by switching on or off at the point where the voltage crosses zero. This minimizes electrical noise and reduces wear on devices. However, proper configuration is key to achieving optimal performance.
To maximize efficiency, start by fine-tuning relay settings. Adjust the time delay to match the specific load characteristics. For instance, resistive loads may require different settings compared to inductive loads. Many overlook this detail, leading to wasted energy. Experimenting with different configurations can reveal nuances in performance.
Another essential factor is ensuring proper heat management. Zero crossing relays can develop heat under continuous use, affecting reliability. Incorporating heat sinks and ensuring adequate airflow can mitigate this issue. Monitoring temperature is crucial. Ignoring it may lead to failures over time. Reflection on these points can lead to significant improvements in overall efficiency.

Zero crossing relays (ZCRs) play a vital role in modern power control applications. One of their most common uses is in lighting control systems. These relays help reduce inrush currents during lamp startups. According to a report by the Energy Efficiency Partnership, using ZCRs can cut energy consumption by up to 30% in commercial lighting systems. This efficiency not only lowers energy bills but also enhances the lifespan of the bulbs.
Another significant application is in heating systems. By integrating ZCRs, electric heaters can achieve more precise temperature control. A study from the International Energy Agency highlighted that this method can improve heating efficiency by around 25%. This capability allows for better energy management, especially in sectors like agriculture, where temperature control is critical for crop growth. However, some challenges remain. Users may find it tricky to select the right relay for their specific needs.
In HVAC systems, ZCRs provide smooth operation of motors. They minimize mechanical stress and prolong equipment life. However, improper use can lead to performance drops. Installing a ZCR needs careful consideration of the load type. Miscalculations can result in frequent relay failures. In essence, while zero crossing relays offer numerous benefits, users must navigate their complexities to harness their full potential.