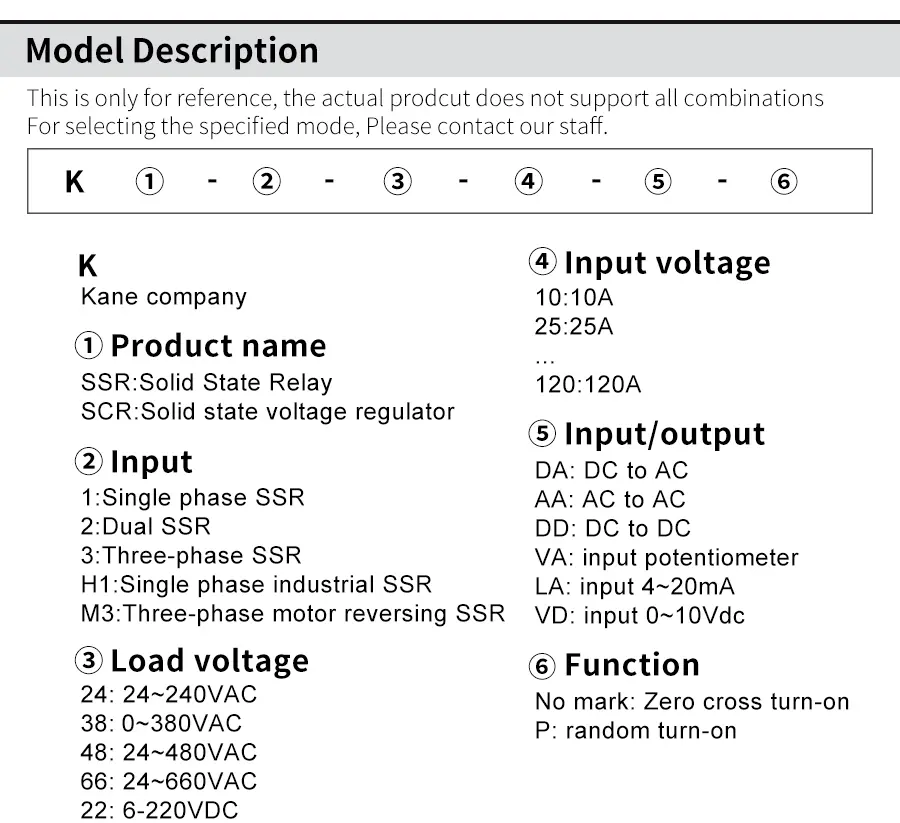
Innovation and Application Prospects of Solid State Relays
In the field of modern industrial automation and power electronics, solid state relays (SSR) are gradually becoming key control components. Compared with traditional mechanical relays, solid state relays have higher reliability, faster response speed and longer service life, so they are widely favored in various applications.
The working principle of solid-state relays is based on semiconductor technology and is mainly divided into two categories: voltage zero-crossing conduction type (zero-crossing type) and random conduction type (random type). Zero-crossing type relays conduct when the voltage waveform passes through the zero point, which can effectively reduce electromagnetic interference and is suitable for occasions with high power quality requirements. Random type relays can conduct at any time and are suitable for applications with high response speed requirements, such as motor control and heating systems.
According to the different output switching elements, solid-state relays can be divided into bidirectional thyristor output type (ordinary type) and unidirectional thyristor anti-parallel type (enhanced type). Ordinary type relays are suitable for most applications, while enhanced types show higher performance and reliability in high-load or high-frequency environments.

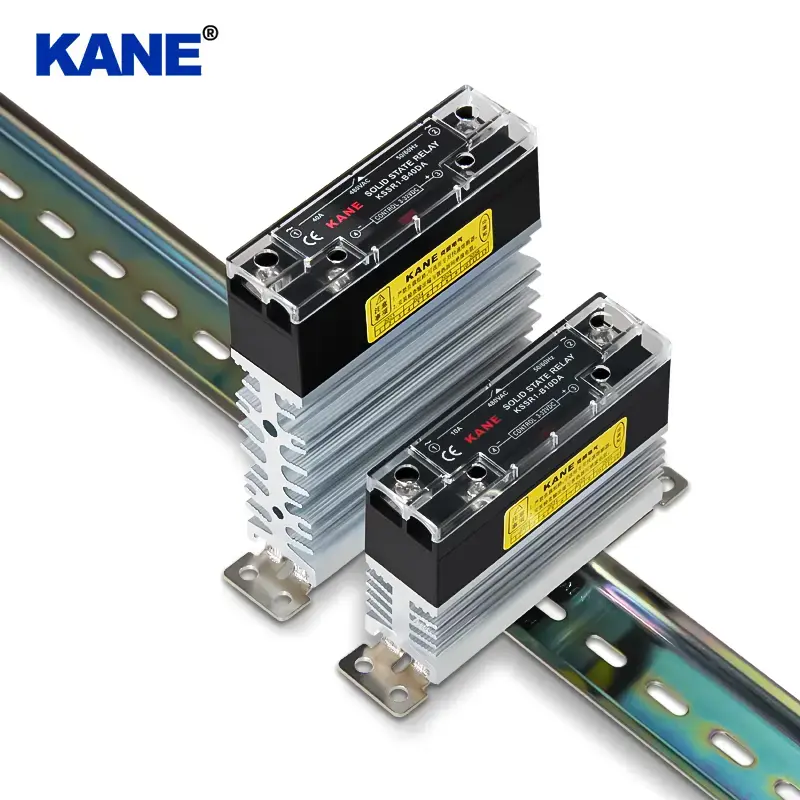
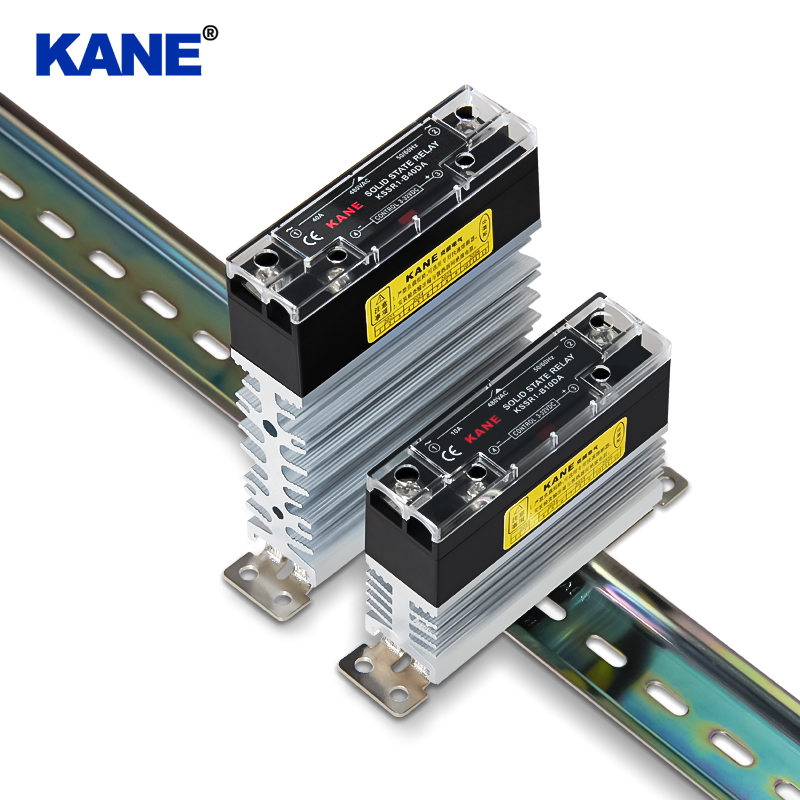
In terms of installation methods, solid-state relays offer a variety of options. The pin-type design on the printed circuit board is easy to integrate, usually uses natural cooling, does not require an additional heat sink, and is suitable for applications with limited space; while the panel-type design fixed on the metal base usually requires a heat sink to ensure stable operation under high power conditions.
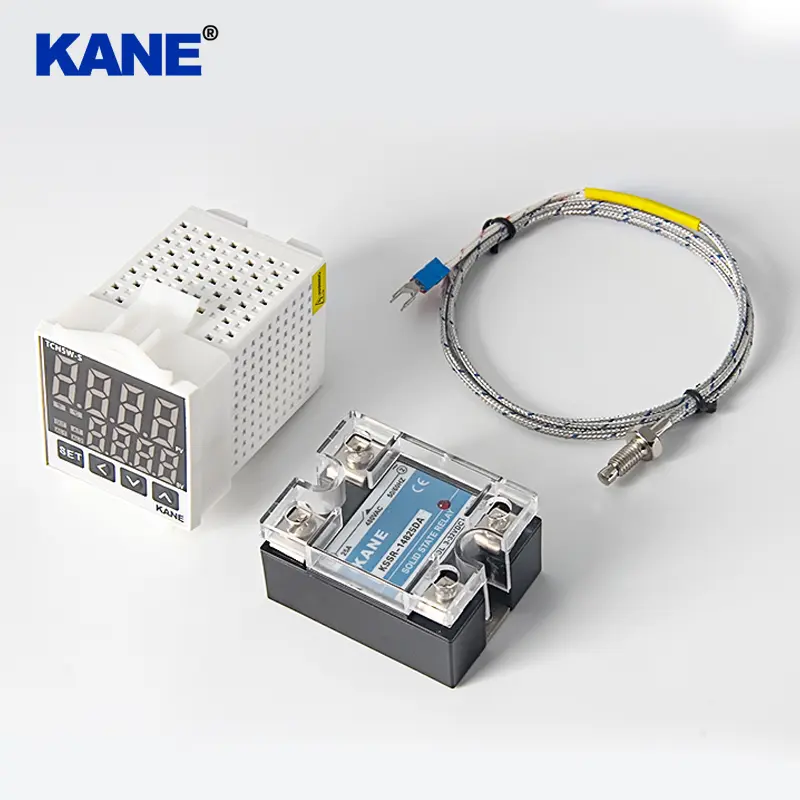
The input design of solid-state relays is becoming increasingly diverse, including constant current type and current limiting type (realized by series resistor) with wide input range (DC3-32V). These designs enable solid-state relays to adapt to the needs of various control signals, further enhancing their application flexibility.
With the continuous development of industrial automation and intelligent manufacturing, the market demand for solid-state relays will continue to grow. Its wide application in power control, temperature regulation, lighting control and other fields indicates that solid-state relays will play a more important role in future technological innovation. Major manufacturers are also constantly developing new solid-state relays to meet the growing market demand and technical challenges.