What are the classifications of SSR solid-state relays?
Classification of SSR Solid State Relay:
AC solid-state relay is an important electronic switching device, widely used in the fields of automation control and power electronics. According to the different switching methods, AC solid-state relays can be divided into two types: voltage zero-crossing conduction type (abbreviated as zero-crossing type) and random conduction type (abbreviated as random type). Zero-crossing type relays conduct when the voltage waveform passes through the zero point, which can effectively reduce electromagnetic interference and current shock, and are suitable for occasions with high requirements for power quality; while random type relays can conduct at any time, which is suitable for applications with high requirements for response speed.
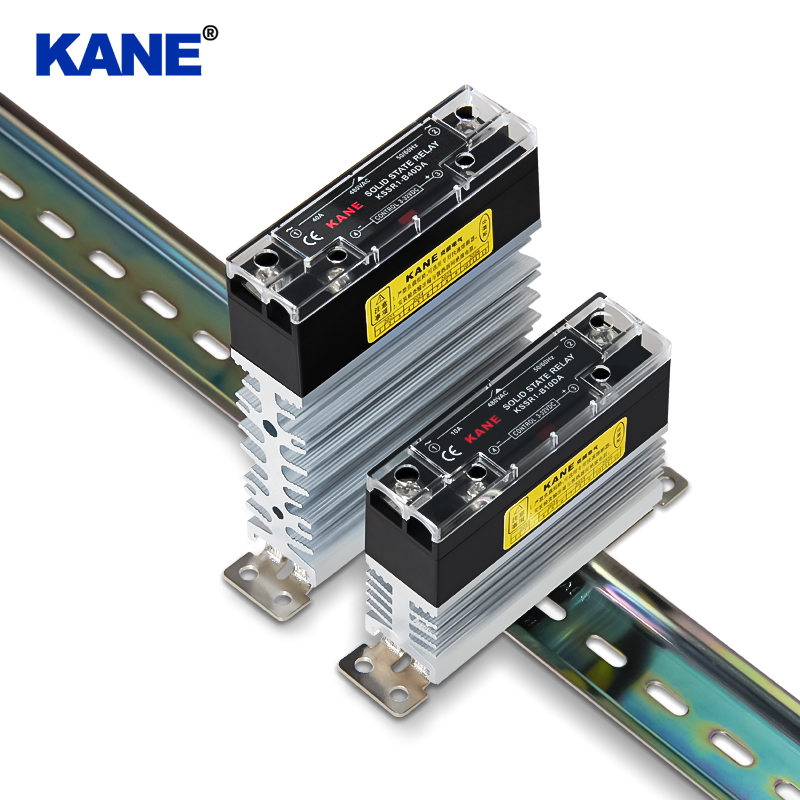
According to the different output switching elements, AC solid-state relays can be divided into bidirectional thyristor output type (ordinary type) and unidirectional thyristor anti-parallel type (enhanced type). Ordinary relays have good versatility and are suitable for most application scenarios; while enhanced types show higher performance and reliability under certain specific conditions and are suitable for high-load or high-frequency applications.
There are also multiple options for AC solid-state relays in terms of installation methods. The pin-type design on the printed circuit board is easy to integrate and install, usually uses natural cooling, does not require an additional heat sink, and is suitable for applications with limited space; while the panel-type design fixed on the metal base usually requires a heat sink to ensure stable operation under high power conditions, and is suitable for use in industrial environments.
There are also many types of input terminals for AC solid-state relays, including constant current type with wide input range (DC3-32V) and current limiting type (realized by series resistor). These different types of input designs enable the relay to adapt to the needs of a variety of control signals, further enhancing its application flexibility and applicability. Through these classifications, users can choose the appropriate AC solid-state relay according to specific application requirements to achieve the best control effect.

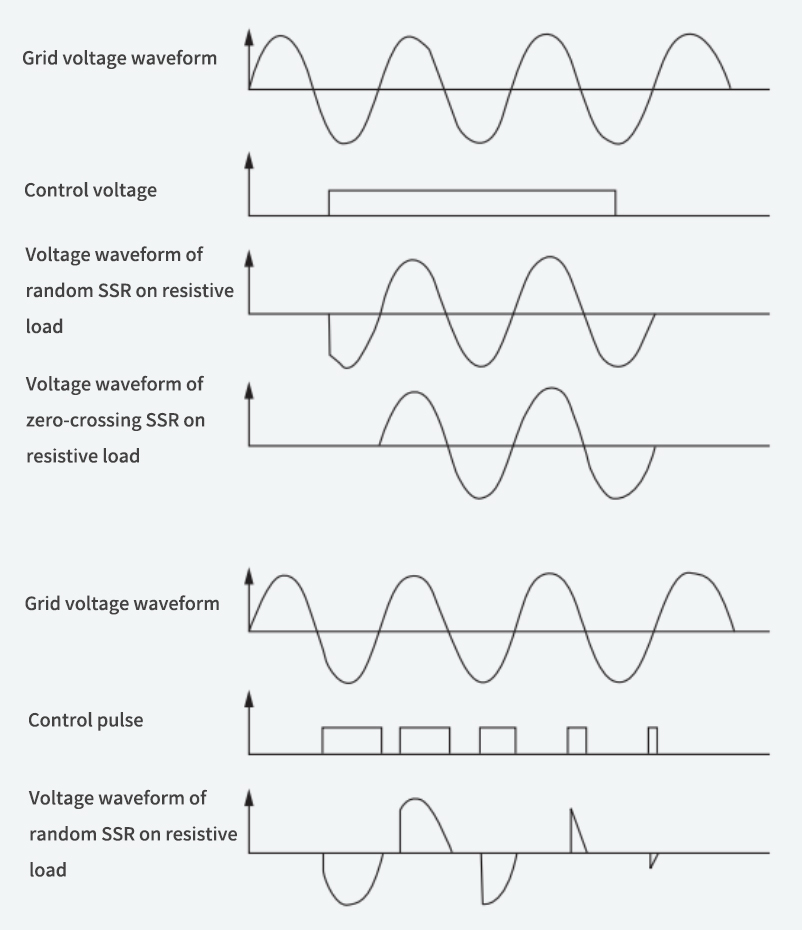
The difference between zero-crossing and random SSRs:
When a valid control signal is applied to the input, the output of the random SSR is immediately turned on (at a speed of microseconds), while the zero-crossing SSR will not turn on until the load voltage crosses the zero region (about ±15V). When the control signal is removed from the input, both the zero-crossing and random SSRs are turned off when the current is less than the holding current.
Although the zero-crossing SSR may cause a maximum half-cycle delay, it reduces the impact on the load and the radio frequency interference generated, making it an ideal switching device and is most widely used in "single-pole single-throw" switching occasions. The characteristic of the random SSR is its fast response speed. It can control the phase-shift trigger pulse to easily change the AC grid voltage, so it can be used in precise temperature control, dimming and other resistive loads and some inductive loads.